Understanding Neuropathic Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Neuropathic pain is a complex condition that affects millions of individuals across the United States and worldwide. Whether you or your loved ones are grappling with neuropathic pain, reading this article will, hopefully, help you see ways to navigate the journey with resilience and hope.
What Is Neuropathic Pain?
Unlike typical pain sensations, which result from tissue damage or inflammation, neuropathic pain stems from dysfunction or damage to the nervous system.
The nervous system is a network responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body. It consists of two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes the nerves outside the CNS. Neuropathic pain can originate from abnormalities in either the peripheral nerves, spinal cord, or brain.
When nerve fibers become damaged or dysfunctional, they may send incorrect signals to pain centers in the body, resulting in neuropathic pain. This aberrant signaling can lead to a variety of symptoms that can significantly impact daily activities and diminish the quality of life for those affected.
What Are the Causes of Neuropathic Pain?
There are numerous conditions and factors that can contribute to neuropathic pain, including the following:
Disease
Several diseases and medical conditions can lead to neuropathic pain. One of the most prevalent is diabetes, which is responsible for approximately 30 percent of neuropathic cases.
Other diseases associated with neuropathic pain include multiple sclerosis (MS), multiple myeloma, and certain types of cancer, such as salivary gland cancer and meningioma (skull base tumor).
Ear infections or ear tumors, such as acoustic neuromas and schwannomas, may also lead to neuropathic pain.
Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune disease, and Lyme disease are two more examples of diseases that may contribute to the development of neuropathic pain.
Injury
Injuries to tissues, muscles, or nerves can also lead to neuropathic pain. Traumatic events, such as accidents or surgeries, can cause lasting damage to the nervous system, resulting in persistent pain even after the initial injury has healed.
Spinal cord injuries,
herniated discs, and nerve compression syndromes are examples of injuries that may precipitate neuropathic pain.
Infection
While infections rarely cause neuropathic pain, certain viral and bacterial infections can lead to this condition. Shingles, caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, can result in postherpetic neuralgia—a type of neuropathic pain that persists after the rash resolves.
Syphilis and HIV infections may cause neuropathic pain as a result of nerve damage or inflammation.
Limb Loss
Phantom limb syndrome is a unique form of neuropathic pain that occurs following amputation. Individuals may experience sensations of pain, tingling, or itching in the missing limb. This phenomenon occurs due to misfiring nerve signals from the residual limb to the brain.
Alcohol Use Disorder
Long-term excessive alcohol consumption can result in various complications, including chronic neuropathic pain.
Alcoholism can lead to neuropathic pain through its detrimental effects on essential nutrients required for proper nerve function. Thiamine, folate, niacin, vitamins B6 and B12, and vitamin E are necessary for the health and integrity of our nervous systems. Excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the levels of these nutrients in the body. Chronic alcohol abuse can deplete levels of these vitamins, impairing nerve function and contributing to the development of alcoholic neuropathy.
Managing alcohol use disorder is essential not only for overall health but also for reducing the risk of neuropathic pain.
Other Causes
Additional factors contributing to neuropathic pain include vitamin B deficiency, carpal tunnel syndrome, thyroid disorders, facial nerve conditions, and spinal arthritis.
What Are the Symptoms of Neuropathic Pain?
Understanding the symptoms of neuropathic pain is important for timely diagnosis and effective treatment or management:
- Burning Sensation: One of the hallmark symptoms of neuropathic pain is a burning sensation that can range from mild to severe. This burning feeling may occur spontaneously or in response to stimuli that would not normally cause pain, such as light touch or temperature changes. Patients often describe it as a constant, throbbing discomfort that can be difficult to alleviate.
- Electric Shock-Like Sensations: Some individuals with neuropathic pain experience sudden, sharp electric shock-like sensations, known as lancinating pain. These jolts of pain can be intense and unpredictable, shooting through affected areas of the body without warning. These sensations can significantly disrupt daily activities and quality of life.
- Tingling or Pins and Needles: Tingling sensations, often described as pins and needles, are another common symptom of neuropathic pain. This sensation can feel like a prickling or crawling feeling under the skin and may be accompanied by numbness or weakness in the affected area. Tingling sensations can be constant or intermittent and may worsen with movement or pressure.
- Numbness or Loss of Sensation: Neuropathic pain can also cause numbness or loss of sensation in the affected area. This loss of feeling may make it difficult for individuals to detect touch, pressure, or temperature changes. Numbness can be particularly problematic, as it increases the risk of injury or trauma to the affected area without the person being aware of it.
- Increased Sensitivity to Touch: While some individuals with neuropathic pain experience numbness, others may develop a heightened sensitivity to touch, a condition known as allodynia. Even light pressure or gentle touch can trigger intense pain or discomfort in affected areas. Allodynia can significantly impact daily activities and make simple tasks, such as getting dressed or taking a shower, challenging.
- Muscle Weakness or Loss of Coordination: In some cases, neuropathic pain may be accompanied by muscle weakness or loss of coordination in the affected area. This can lead to difficulty performing fine motor tasks or maintaining balance and stability. Muscle weakness may worsen over time if the underlying cause of neuropathic pain is not addressed.
What Are the Treatment Options for Neuropathic Pain?
Managing neuropathic pain can be challenging, but there are several treatment options available to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
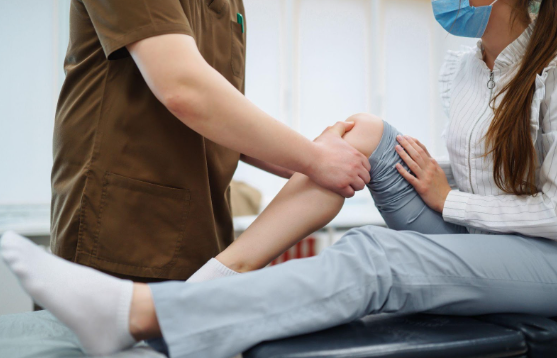
Physical therapy can be beneficial for neuropathic pain, especially when it is associated with conditions such as diabetic neuropathy or nerve compression syndromes. Therapeutic exercises, stretching, and manual techniques can help improve mobility, reduce stiffness, and alleviate pain.
Making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and managing stress, can all contribute to reducing neuropathic pain. Avoiding alcohol and tobacco, which can exacerbate pain symptoms, is also important.
At
Pain Treatments Centers of America, we strive to help our patients cope with neuropathic pain.
Contact us today.